|

|

|
HR MRI with myelographic pictures
Here is a link to a publication in which you are to see pictures for all diseases dealing with dural tube and nerve problems, such as Tarlovcyst, Arachnoïditis, Tethered Cords, ....
those are the best pictures that are existing for all that till now....
the link is to the place from where you can download those pictures..
http://www.ajronline.org/cgi/reprint/179/2/515
________________________________________
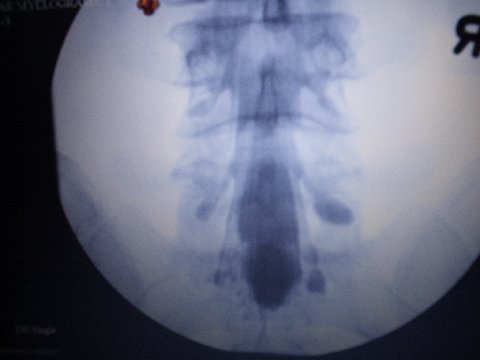
MYELOGRAPHY :
Myelography or saccoradiculography
• The Myelography or saccoradiculography studies spinal cord and the beginning of the nervous roots which are born at this level.
• This examination is useful in the assessment of neurological pain such as sciatic nerves pain that are not relieved by any treatment or requiring a surgical operation.
• It seeks signs of neurological compression. It makes it possible to determine the precise level of the attack, its cause (slipped disc, tumour, abscess, and haematoma, or other causes.) and the severity of lesions observed.
This examination uses x-rays and one contrast product containing iodine.
Its principle consist to opacify and visualize contours of spinal cord . The product of contrast is injected into the dural tube located at the center of the spinal column. It diffuses and opacify inside of the spinal cord so the cause of the pain is to be visible on the pictures because of the properties of iodine opaque of iodine.
In the room of examination, one finds:
• The apparatus which is composed of a tilting table above which a hinged jib provided with a tube with x-rays move.
• The control panel behind which is medical personnel
• It is a doctor specialist in radiology which practises this examination.
• During the examination:: the skin at the point of puncture is disinfected. With a fine needle, the radiologist pricks with the bottom of the back between two vertebrae then progresses to the rachidian channel as for one lumbar puncture. At the time of this gesture, it is advisable not to move! After having withdrawn small quantity of liquid, the product of contrast is injected and the needle is withdrawn. A series of pictures is made in various positions. The examination lasts approximately 30 minutes. Right after, a scan is made for other pictures to be made and another view….
• After the examination, you will have to remain lengthened on the back one day to avoid headaches. Drink much water for natural elimination of the product of contrast.
• Results: The radiologist will give you one first comment. It will send its final report to your doctor treating as soon as possible. This last will explain you them results and will give you the action to be taken.
• The puncture in the bottom of the back is the moment more unpleasant but it lasts only a short moment. A local anaesthesia can be practised as well as the application of an anaesthetic gel
• The injection of the product of contrast can give you headaches during several hours. Drugs against the pain (analgesics) will be prescribed if needed. It will be necessary to remain lengthened on the back one day after the examination.
If this exam is made in order to know is Tarlovcyst is symptomatic, there are pictures made immediately, then 3 hours later, 6 hours later, 9 hours later and 12 hours later, but only pictures. It is made that way to discover how quickly the cyst is filling or if not filling and also to discover how fast the contrast product is going off the cyst…
So the neuroradiologist can say what kind of cyst it is and If it is possible to make some procedure to relieve the patient from the pain….
It is only made in hospitals where a team is aware and treating tarlovcysts.
about contrast products:
Pantopaque (iophendylate) is a very old CM used for mielography that was introduced in clinical practice in 1944!!!! . It's an oil based non soluble ionic iodinated CM. Due to this physicochemical properties, this contrast agent was accumulated in the intraspinal space and was led to a high risk of arachnoiditis, meningitis, seizures, etc besides pulmonary embolism. The history of iophendyalte is sad and seems full of deep movements.
New CM for mielography and others diagnostic tests (i.e. iohexol, iodixanol, iopromide, etc) are also iodinated but unlike Pantopaque, new CM are water soluble, non-ionic and has a low osmolality. These properties make them very well tolerated. Then, although spinal injections are not potentially devoid of risks, in comparison to Pantopaque are practically insignificant.
|
|